 ARCHITECTURE
ARCHITECTURE
Over the last few years, technological innovations have profoundly altered architectural surveying methods, focusing on the study based on existing systems such as laser scanners, digital photogrammetry, etc. At the expense of direct examination of the artefact, our philosophy of investigation is based on careful integration of technological data with in-situ graphic documentation, enabling 2D / 3D representation based on as much information as possible.
Over the last few years, technological innovations have profoundly altered architectural surveying methods, focusing on the study based on existing systems such as laser scanners, digital photogrammetry, etc. At the expense of direct examination of the artefact, our philosophy of investigation is based on careful integration of technological data with in-situ graphic documentation, enabling 2D / 3D representation based on as much information as possible.
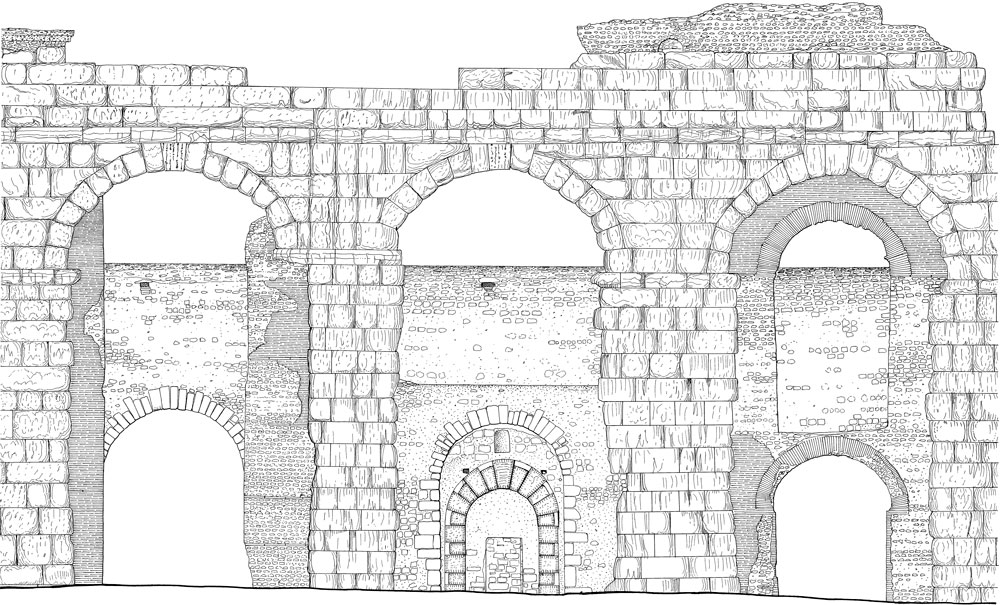

In particular, regarding the three-dimensional representation of architectural structures, their characteristics and the purpose for which research is directed determine the choice of methods to be used.
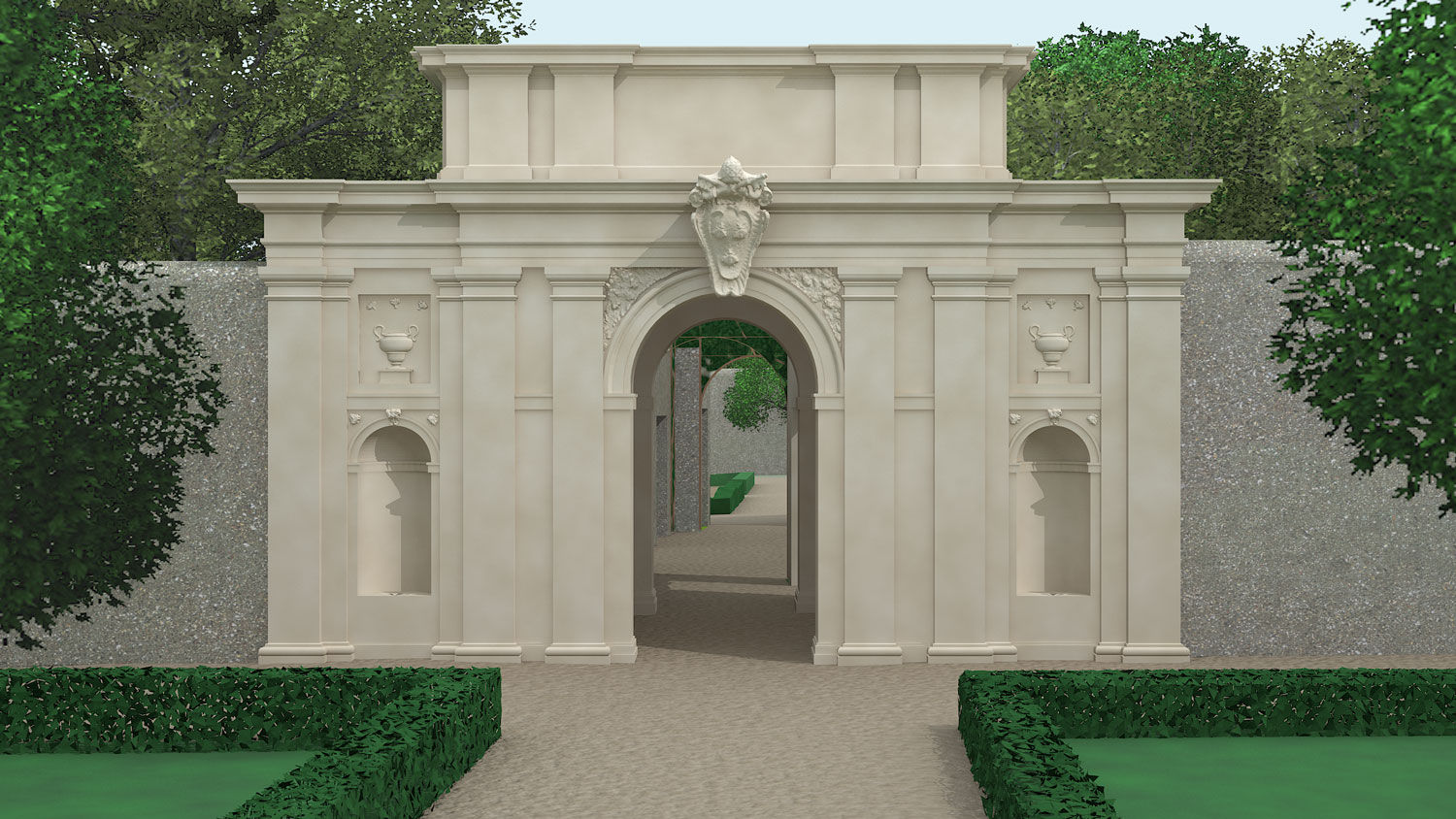
The technical means at our disposal now allow you the achievement of a great deal of realism, so the most important task to define is without doubt the choice of the level of detail you want to achieve in 3D modelling. Depending on the results you want to achieve, you can create schematic 3D models with a minimum level of detail (useful for interactive navigation), up to high-definition models (useful for studies of degradation and for a ‘ deep knowledge of the historical phases of the artefact).
Studio 3R, collaborating closely with officials responsible for the protection of property and experts of the sector, has always sought the best technology and analytical solution aimed at achieving the objective of the study, on a case-by-case basis.
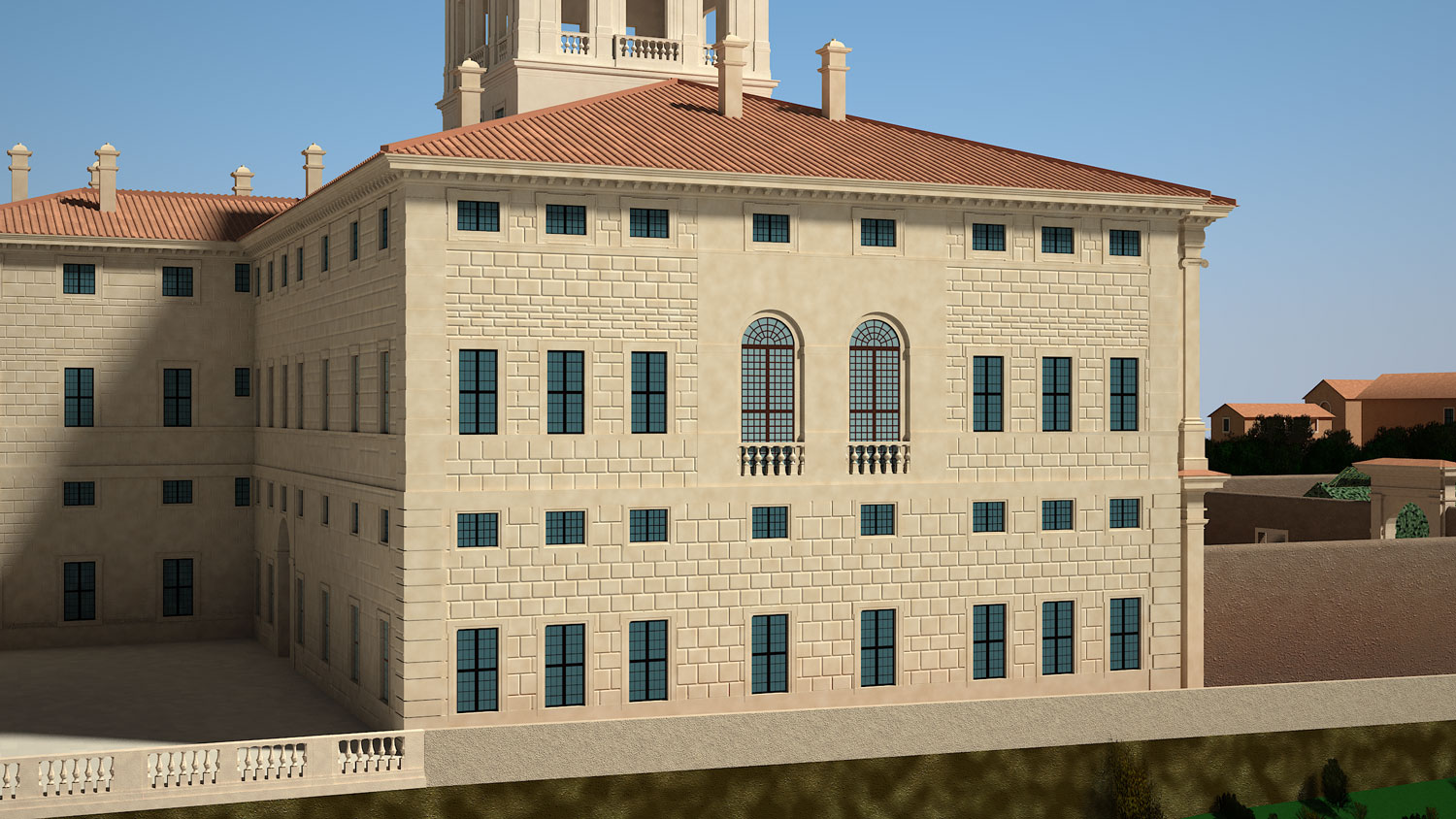
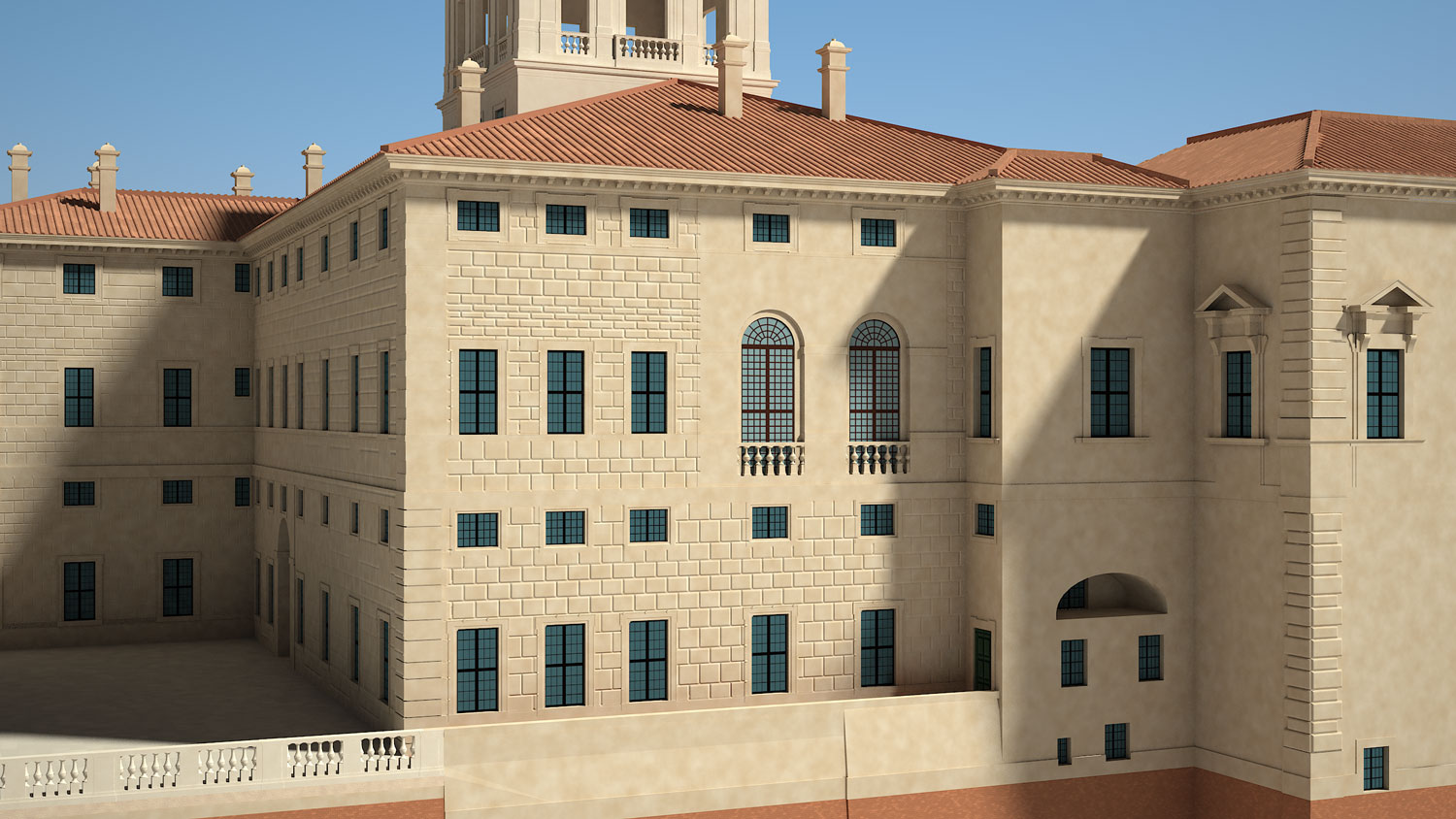
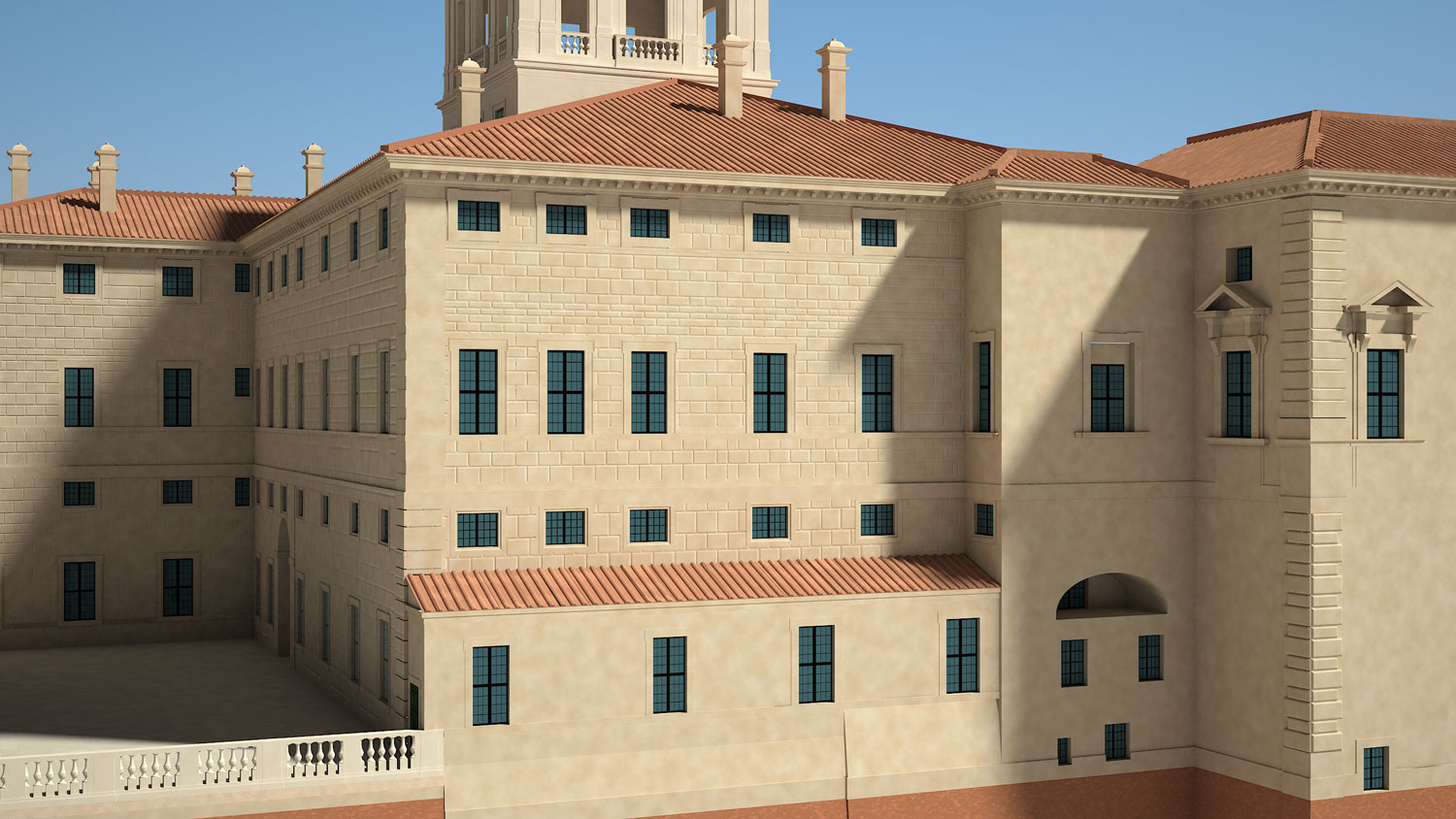
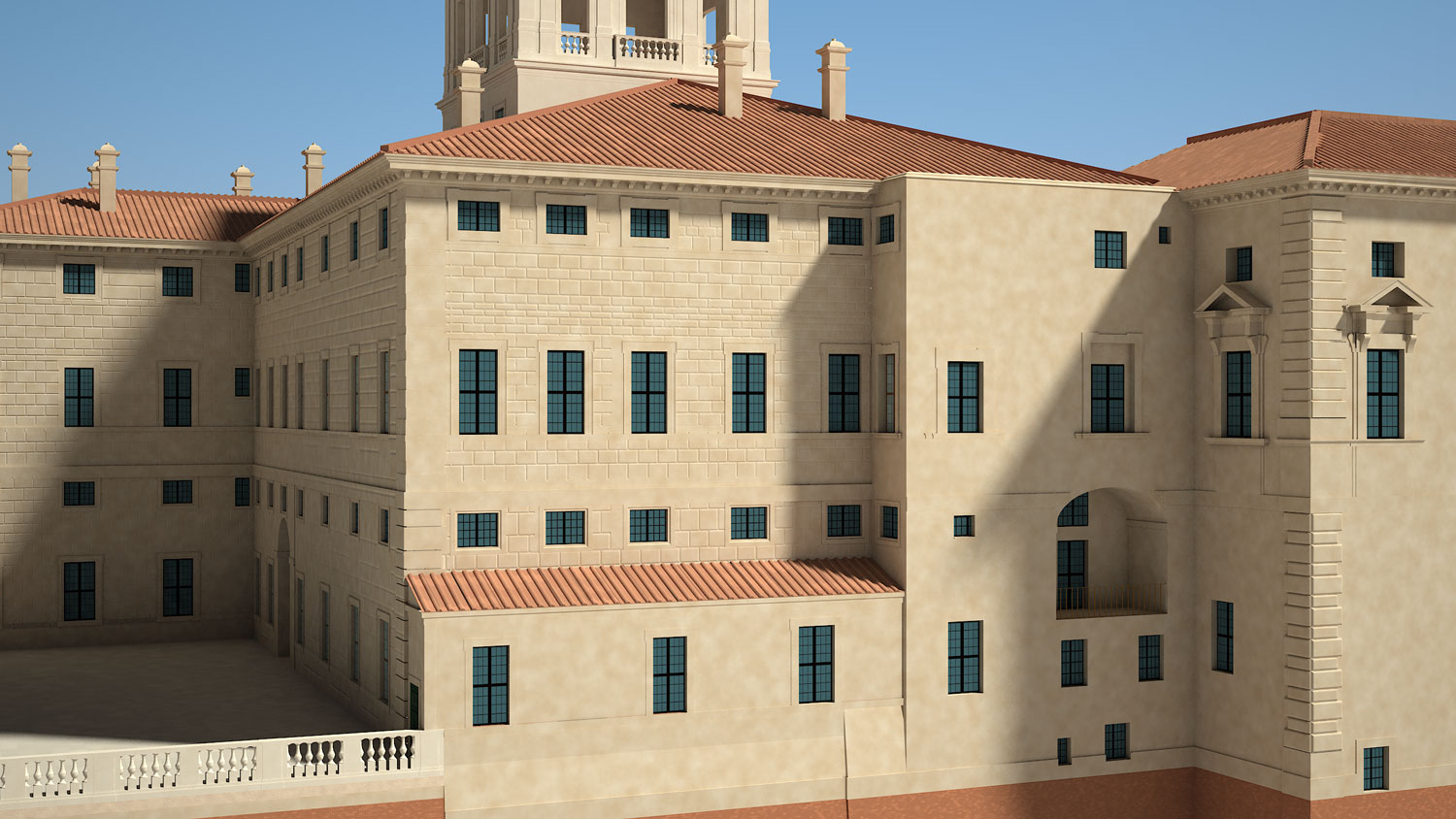
An example of this is the 3D models of Quirinale structures that do not only document the current state of the buildings, but are based on the study of the historical reconstruction of the various phases during different times; In this case part of the data was extracted from images, drawings and archive sources.



